Language model collaboration for relation extraction from classical Chinese historical documents
Aug 1, 2025·
 ,
,
·
1 min read
,
,
·
1 min read
TANG Xuemei (唐雪梅)
Linxu Wang
Jun Wang
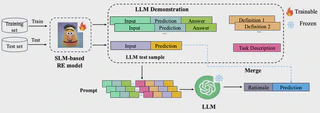 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
Classical Chinese historical documents are invaluable for Chinese cultural heritage and history research, while they remain underexplored within natural language processing (NLP) due to limited annotated resources and linguistic evolution spanning thousands of years. Addressing the challenges presented by this low annotated resource domain, we develop a relation extraction (RE) corpus that preserves the characteristics of classical Chinese documents. Utilizing this corpus, we explore RE in classical Chinese documents through a collaboration framework that integrates small pre-trained language models (SLMs), such as BERT, with large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3.5. SLMs can quickly adapt to specific tasks given sufficient supervised data but often struggle with few-shot scenarios. Conversely, LLMs leverage broad domain knowledge to handle few-shot challenges but face limitations when processing lengthy input sequences. Combining these complementary strengths, we propose a “train-guide-predict” collaboration framework, where a small language model corporate with a large language model (SLCoLM). This framework enables SLMs to capture task-specific knowledge for head relation categories, while LLMs offer insights for few-shot relation categories. Experimental results show that SLCoLM outperforms both fine-tuned SLMs and LLMs using in-context learning (ICL). It also helps mitigate the long-tail problem in classical Chinese historical documents.
Type
Publication
Information Processing & Management
Click the Cite button above to demo the feature to enable visitors to import publication metadata into their reference management software.
Create your slides in Markdown - click the Slides button to check out the example.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.